Hack Chat 0x02: Introduction to 3D Printing
-
Steag Center for Smart Technologies is organizing second HackChat exclusively for the Rajagiri students.
This week we are going to learn about 3D Printing Technologies.
Venue: Steag Center, KE Block Extension. Rajagiri Engineering college.
Date: Feb-13-2020
Time: 5:00 PM to 5:30 PMRegister here: bit.ly/hackchat2
No Registration Fee

-
3D PRINTING
3D Printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital design. There are different 3D printing technologies and materials you can print with, but all are based on the same principle: a digital model is turned into a solid three-dimensional physical object by adding material layer by layer. In an additive process, an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object.(Source:- https://www.3dhubs.com)

-
There is a different way to print a 3D object.
Stereolithography(SLA)
This process that converts liquid plastic into solid objects.

These 3D printing technologies are also available in desktop 3D printers. Materials are limited to resins, but new varieties have appeared recently providing strength or flexibility to the final objects.SLA and DLP 3D printers produce highly accurate parts with smooth surface finishes and are commonly used for highly detailed sculptures, jewellery moulds, and prototypes. Because of their relatively small size, they are not recommended for printing large objects.(Source:- https://www.3dhubs.com)
Material Jetting (PolyJet and MultiJet Modeling)
Material Jetting (Stratasys PolyJet and 3D Systems MultiJet Modeling) technologies are similar to inkjet printing, but instead of jetting drops of ink onto paper, these 3D printers jet layers of liquid photopolymer onto a build tray and cure them instantly using UV light.

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a laser to melt and solidify layers of powdered material into finished objects.

Fused-deposition moulding (FDM)
The FDM printing process starts with a string of solid material called the filament. This line of filament is guided from a reel attached to the 3D printer to a heated nozzle inside of the 3D printer that melts the material. Once in a melted state, the material can be extruded on a specific and predetermined path created by the software on the computer. As the material is extruded as a layer of the object on this path, it instantly cools down and solidifies – providing the foundation for the next layer of material until the entire object is manufactured.

As the cheapest 3D printing technology on the market, FDM also offers a wide variety of plastic-based materials in a rainbow of colors including ABS, PLA, nylon and even more exotic material blends including carbon, bronze or wood.(Source :- https://www.3dhubs.com)
-
PRINTING MATERIAL
The material used will affect the mechanical properties and accuracy of the printed part, but also its price. The most common FDM materials are summarized in the table below. (Source:- https://www.3dhubs.com/knowledge-base/introduction-fdm-3d-printing

-
FlashForge Pro
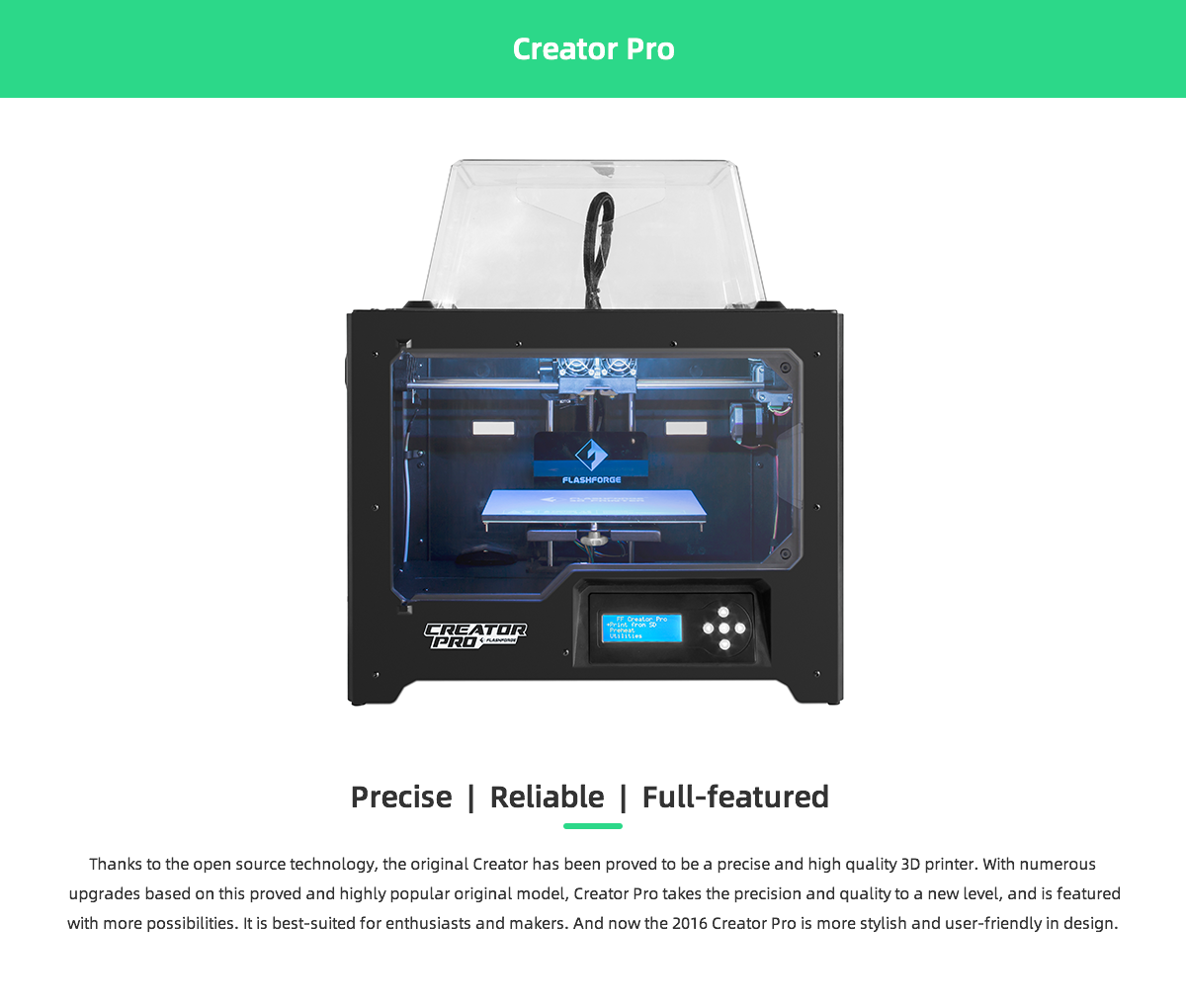
FlashForge 3D Printer Creator Pro, Metal Frame Structure, Acrylic Covers, Optimized Build Platform, Dual Extruder W/2 Spools, Works with ABS and PLA.

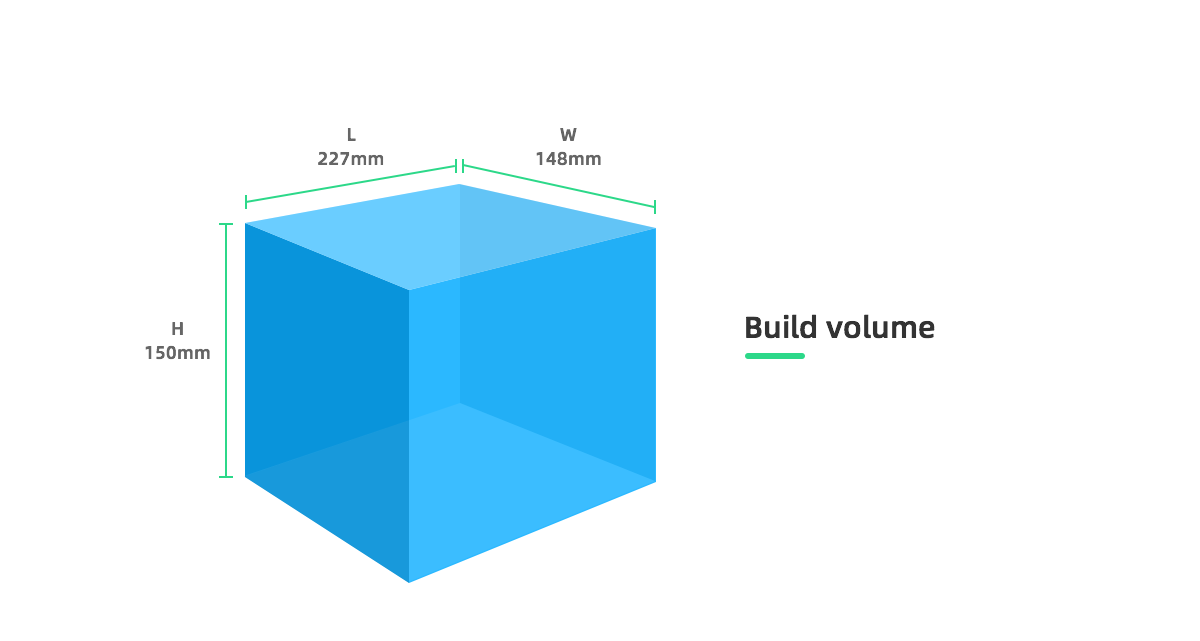

Source: https://www.flashforge.com/consumer/detail/Creator Pro?id=4




