Hack Chat 0x03: Introduction to CNC Machining
-
What is a CNC Machine?
CNC stands for Computer Numeric Control it is a process used in the manufacturing sector that involves the use of computers to control machine tools. Tools that can be controlled in this manner include lathes, mills, routers and grinders.
The process involves creating a CAD(Computer-Aided Design) file of the desired object. Then a specialized CAM (computer-aided Manufacturing) software is required to convert the 3D CAD file into a set of codes which the machines can understand.
CNC machining language, called G-code essentially controls all features like feed rate, coordination, location and speeds. With CNC machining, the computer can control exact positioning and velocity.

In CNC, machines are operated via numerical control, wherein a software program is designated to control an object. The language behind CNC machining is alternately referred to as G-code, and it’s written to control the various behaviours of a corresponding machine, such as the speed, feed rate and coordination. (src: https://astromachineworks.com/what-is-cnc-machining/)
-
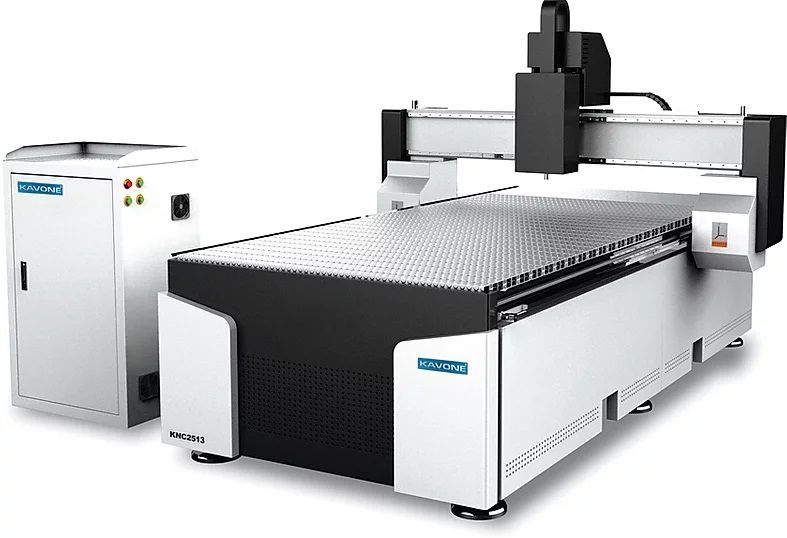
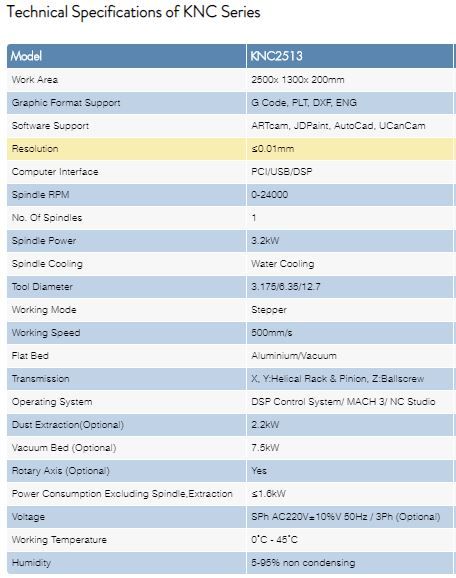
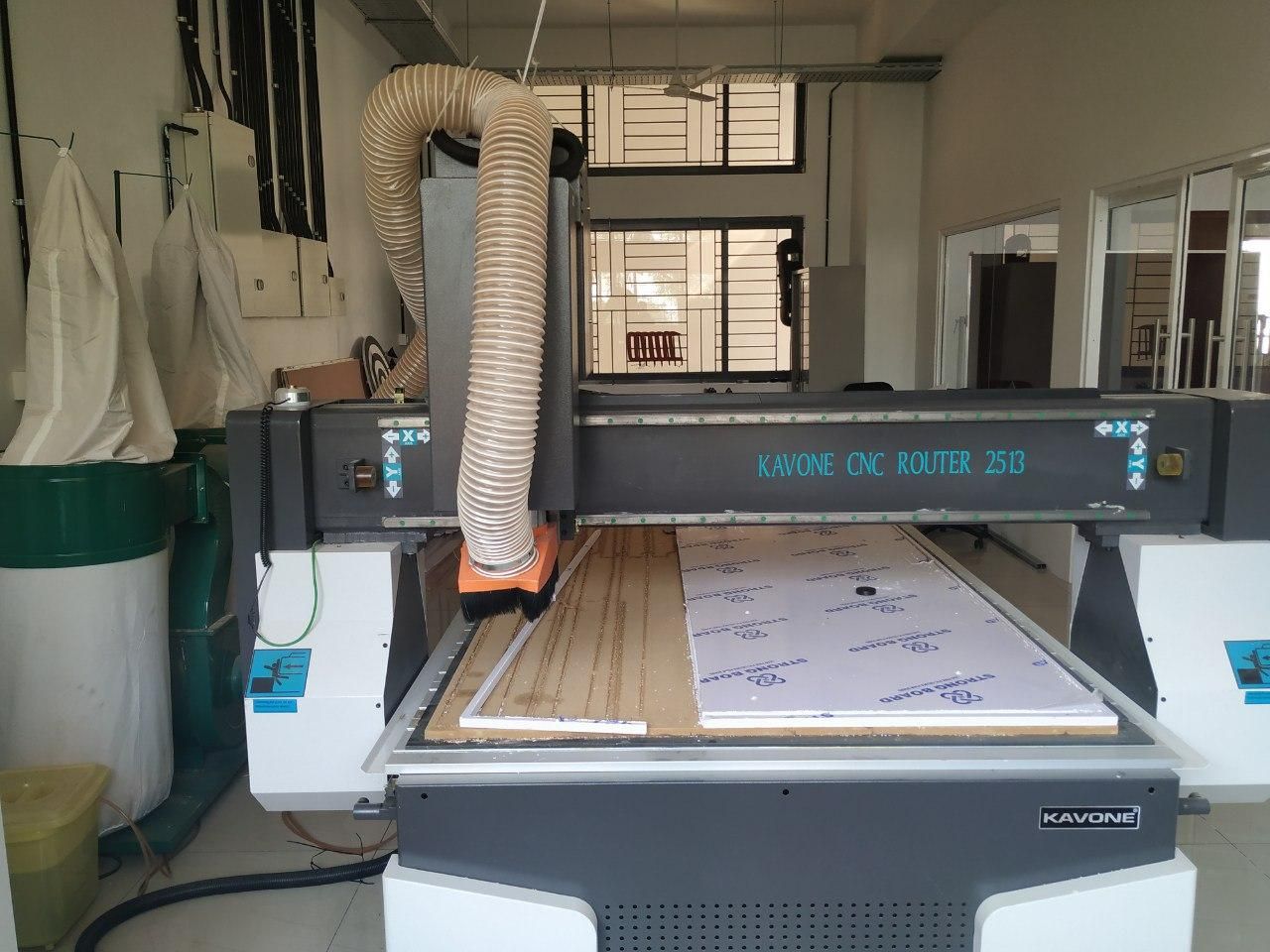
The Center is equipped with Kavone KNC Series CNC Router.

-

-
Tool Specifications
Bit material: Router bits used in Shopbot are made from a variety of materials such as solid carbide, carbide-tipped steel, and high-speed steel.
Flute type: There are four basic flute types: Straight, spiral up-cut, spiral down-cut, and compression

-
Drill bit Vs Endmills: A drill bit needs to cut straight into the material hence will have teeth at tip. But an Endmill needs to cut from the sides also, that means it needs to have a cutting edge spiralling all the way up to the flute.

-
Upcut & Downcut

In an Upcut type end mill the teeth on the flute will point upwards. This means that the end mill is cutting and drawing out the wood through the flute. This is good for cutting deep into the stock. But this leaves a bad surface finish on the top of the surface.
A downcut type end mill has teeths that point downward on the flute. This means that the end mill will cut and try to push the material into the stock. This will give good surface finish on the top, but it is not very efficient at removing material.
-
Flat/ball end

flat end leaves flat surface profile on the stock and are good for removing large volume of material, but steps are formed when used for making curved surfaces. Ball end leaves curved surfaces and forms smooth curved finish while cutting cavities. They are used for finishing cuts.