@zainmuhammed
this is the code
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <U8x8lib.h>
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
static const int RXPin = 1, TXPin = 2;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// The serial connection to the GPS device
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin);
U8X8_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_HW_I2C u8x8(/*reset=*/U8X8_PIN_NONE);
// U8X8_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_SW_I2C u8x8(/*clock=*/ SCL, /*data=*/ SDA, /*reset=*/ U8X8_PIN_NONE); // OLEDs without Reset of the Display
static char recv_buf[512];
static bool is_exist = false;
static bool is_join = false;
static int led = 0;
static int at_send_check_response(char *p_ack, int timeout_ms, char *p_cmd, ...) {
int ch;
int num = 0;
int index = 0;
int startMillis = 0;
va_list args;
char cmd_buffer[256]; // Adjust the buffer size as needed
memset(recv_buf, 0, sizeof(recv_buf));
va_start(args, p_cmd);
vsprintf(cmd_buffer, p_cmd, args); // Format the command string
Serial1.print(cmd_buffer);
Serial.print(cmd_buffer);
va_end(args);
delay(200);
startMillis = millis();
if (p_ack == NULL) {
return 0;
}
do {
while (Serial1.available() > 0) {
ch = Serial1.read();
recv_buf[index++] = ch;
Serial.print((char)ch);
delay(2);
}
if (strstr(recv_buf, p_ack) != NULL) {
return 1;
}
} while (millis() - startMillis < timeout_ms);
return 0;
}
static void recv_prase(char *p_msg) {
if (p_msg == NULL) {
return;
}
char *p_start = NULL;
int data = 0;
int rssi = 0;
int snr = 0;
p_start = strstr(p_msg, "RX");
if (p_start && (1 == sscanf(p_start, "RX: \"%d\"\r\n", &data))) {
Serial.println(data);
u8x8.setCursor(2, 4);
u8x8.print("led :");
led = !!data;
u8x8.print(led);
if (led) {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
}
}
p_start = strstr(p_msg, "RSSI");
if (p_start && (1 == sscanf(p_start, "RSSI %d,", &rssi))) {
u8x8.setCursor(0, 6);
u8x8.print(" ");
u8x8.setCursor(2, 6);
u8x8.print("rssi:");
u8x8.print(rssi);
}
p_start = strstr(p_msg, "SNR");
if (p_start && (1 == sscanf(p_start, "SNR %d", &snr))) {
u8x8.setCursor(0, 7);
u8x8.print(" ");
u8x8.setCursor(2, 7);
u8x8.print("snr :");
u8x8.print(snr);
}
}
void setup(void) {
u8x8.begin();
u8x8.setFlipMode(1);
u8x8.setFont(u8x8_font_chroma48medium8_r);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.begin(GPSBaud);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
Serial1.begin(9600);
Serial.print("E5 LORAWAN TEST\r\n");
u8x8.setCursor(0, 0);
if (at_send_check_response("+AT: OK", 100, "AT\r\n")) {
is_exist = true;
at_send_check_response("+ID: DevEui", 1000, "AT+ID=DevEui,\"xxxxx\"\r\n"); // replace 'xxxxxxxxxxxxx' with your DevEui
at_send_check_response("+ID: AppEui", 1000, "AT+ID=AppEui,\"xxxxxxx\"\r\n"); // replace 'xxxxxxxxxxxxx' with your AppEui
at_send_check_response("+KEY: APPKEY", 1000, "AT+KEY=APPKEY,\"xxxxxxxxx\"\r\n"); // replace 'xxxxxxxxxxxxx' with your AppKey
at_send_check_response("+ID: DevAddr", 1000, "AT+ID=DevAddr\r\n");
at_send_check_response("+ID: AppEui", 1000, "AT+ID\r\n");
at_send_check_response("+MODE: LWOTAA", 1000, "AT+MODE=LWOTAA\r\n");
at_send_check_response("+DR: IN865", 1000, "AT+DR=IN865\r\n"); // Change FREQ as per your location
at_send_check_response("+CH: NUM", 1000, "AT+CH=NUM,0-2\r\n");
at_send_check_response("+CLASS: C", 1000, "AT+CLASS=A\r\n");
at_send_check_response("+PORT: 8", 1000, "AT+PORT=8\r\n");
delay(200);
u8x8.setCursor(5, 0);
u8x8.print("LoRaWAN");
is_join = true;
} else {
is_exist = false;
Serial.print("No E5 module found.\r\n");
u8x8.setCursor(0, 1);
u8x8.print("unfound E5 !");
}
u8x8.setCursor(2, 4);
u8x8.print("led :");
u8x8.print(led);
}
void loop(void) {
if (is_exist) {
int ret = 0;
if (is_join) {
ret = at_send_check_response("+JOIN: Network joined", 12000, "AT+JOIN\r\n");
if (ret) {
is_join = false;
} else {
at_send_check_response("+ID: AppEui", 1000, "AT+ID\r\n");
Serial.print("JOIN failed!\r\n\r\n");
delay(5000);
}
} else {
gps.encode(ss.read());
float a=gps.location.lat();
float b=gps.location.lng();
Serial.println(a);
Serial.println(b);
char cmd[128];
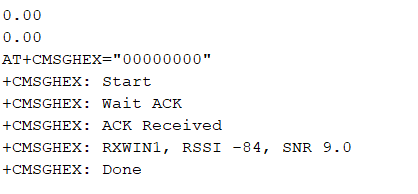
sprintf(cmd, "AT+CMSGHEX=\"%04X%04X\"\r\n", (float)a,(float)b);
ret = at_send_check_response("Done", 5000, cmd);
if (ret) {
recv_prase(recv_buf);
} else {
Serial.print("Send failed!\r\n\r\n");
}
delay(5000);
}
} else {
delay(1000);
}
}